What is a Customs Duty?
A customs duty, also known as a tariff, is a tax imposed by governments on imported goods when they arrive at the border. These duties are charged to importers in the country where the goods are being imported. The term "customs duties" is often used interchangeably with terms like "customs" or "tariffs," and they represent an important source of government revenue.
Why are customs duties imposed?
Customs duties are an effective tool for achieving several economic and political objectives. Firstly, they serve as a major source of government revenue, with the collected funds used to finance various government projects. Secondly, customs duties act as an economic protection barrier by making imported products less competitive compared to local products. By increasing the cost of imported goods, they help boost demand for domestic products and support national industries.
These duties are imposed under trade agreements between countries, where customs duties may be reduced or certain products completely exempted. Such tariffs aim to promote trade cooperation between countries involved in bilateral or multilateral trade agreements. They can help facilitate trade between nations and strengthen economic relationships.
Example: Under free trade agreements such as NAFTA (North American Free Trade Agreement), products traded between the three countries may be exempt from customs duties or subject to reduced rates.
Why are customs duties important?
Customs duties are considered important for several reasons:
- Protecting domestic industries: By imposing duties on imported products, countries can protect local industries from unfair foreign competition.
- Increasing government revenue: Duties serve as an important source of government income, especially in countries that rely on international trade.
- Impact on local prices: Duties may lead to higher prices in the domestic market, which can affect consumers' purchasing power.
Types of Customs Duties and Their Impact on Trade
Customs duties are among the most important tools used by countries to regulate international trade. Duties are imposed on imported products to protect them from foreign competition or to regulate local markets. There are four main types of duties, which differ based on how they are applied to imported or exported goods:
1. Ad valorem tariff
This is one of the most common types of customs duties. A tax is imposed on imported products based on their market value. In other words, the higher the value of the product, the higher the customs duty imposed. The duty is calculated as a percentage of the actual value of the imported or exported product. This type of duty ensures that the tax is fair for all products, regardless of their quantity or size.
Example: If the customs duty is 10% based on value and the product price is $1,000, the duty would be $100.
2. Specific tariff
This type of duty is imposed at a fixed rate on each unit of the imported product, regardless of its value. These duties are applied based on the number of units, weight, or volume of the imported goods. They are particularly suitable for products whose value is difficult to assess accurately.
Example: A specific customs duty of $5 may be imposed on each unit of the imported product.
3. Compound tariff
As the name suggests, this type of duty is a combination of the previous two types (ad valorem and specific duties). A tax is imposed on the product based on a percentage of its value as well as a fixed amount depending on its quantity or volume. This type is sometimes used for more precise regulation of certain markets.
Example: If the compound customs duty consists of 5% of the product's value and $3 per unit, then for a product valued at $1,000 with 50 units, the duty would be $50 (5% of the value) plus $150 ($3 per unit).
4. Preferential tariff
A preferential tariff is a type of customs duty in which a country grants preferential treatment to a specific country or group of countries by reducing or eliminating customs duties on certain imported goods from those countries, compared to the regular tariff applied to the same goods imported from other countries.
How do customs duties affect the economy?
Although customs duties can benefit the local economy in some cases, they also have negative effects, such as:
- Increased production costs: If companies import raw materials or intermediate products, duties can lead to higher production costs.
- Pressure on consumers: Higher duties may lead to increased prices on imported products, which can reduce consumers' purchasing power.
Difference between Code HS And the Customs Tariff Code:
| Feature | HS Code (Harmonized System) | Customs Tariff Code |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An internationally recognized classification of products in international trade. | A code used to determine the customs duties imposed on imported products. |
| Field | It is generally used to classify products in international trade. | It is used to determine the amount of customs duties on imported products. |
| Application | It is used in all countries as part of a unified system. | It varies from country to country according to each nation’s system. |
| goal | It aims to standardize the classification of products worldwide. | It aims to determine the customs duties and fees applicable to goods. |
| Responsible Authority | It was developed by the World Customs Organization (WCO). | It is determined by the customs authorities in each country according to the local system. |
In simple terms:
• HS Code = How to identify the product
• Customs duty = How much to pay on it
Customs tariff code in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia:
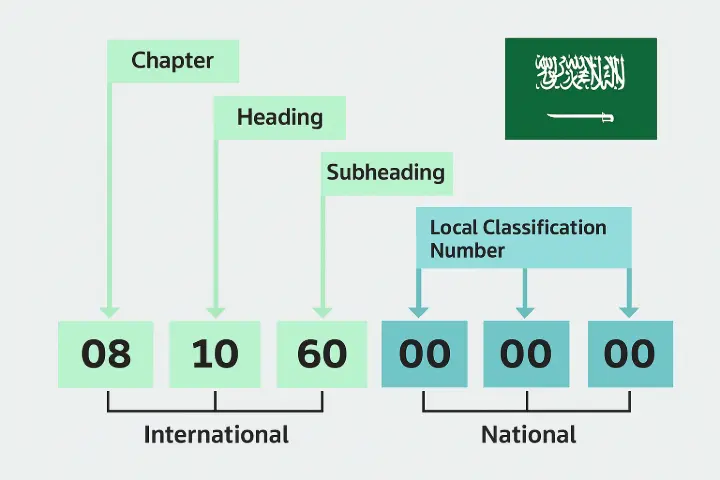
In Saudi Arabia, the HS code is the Saudi customs tariff code. This code consists of 12 digits and is regulated by the General Authority of Zakat and Tax and Customs.
- The first six digits: Follow the same classification as the internationally recognized HS code established by the World Customs Organization (WCO).WCO).
- The first six digits: Follow the same classification as the internationally recognized HS code established by the World Customs Organization (WCO).
- The last four digits: Are specific to the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The additional digits after the first six in the HS Code are added by each country for local purposes, most importantly to determine the customs duty.
To find the Saudi customs tariff codes for exported products, you……can use the official Saudi Customs search tool..
Summary :
Customs duties are an important tool in international trade, and each type has its own uses and purposes. These duties can help protect the local economy and increase government revenue, but they can also affect local prices and consumers' purchasing power. Therefore, it is essential to set duties carefully to ensure a balance between economic benefits and consumer protection.

Customs Duty and Its Difference from the HS Code